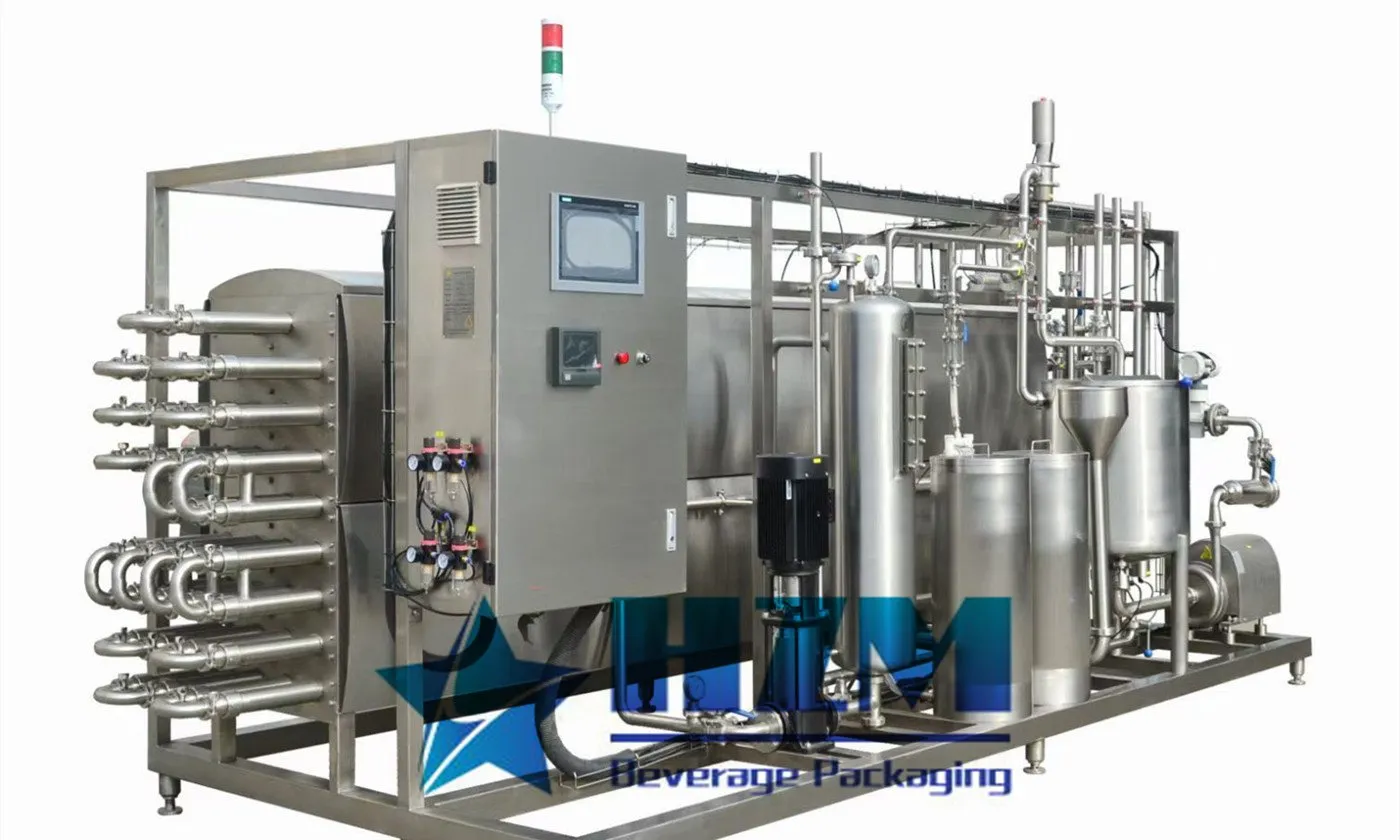
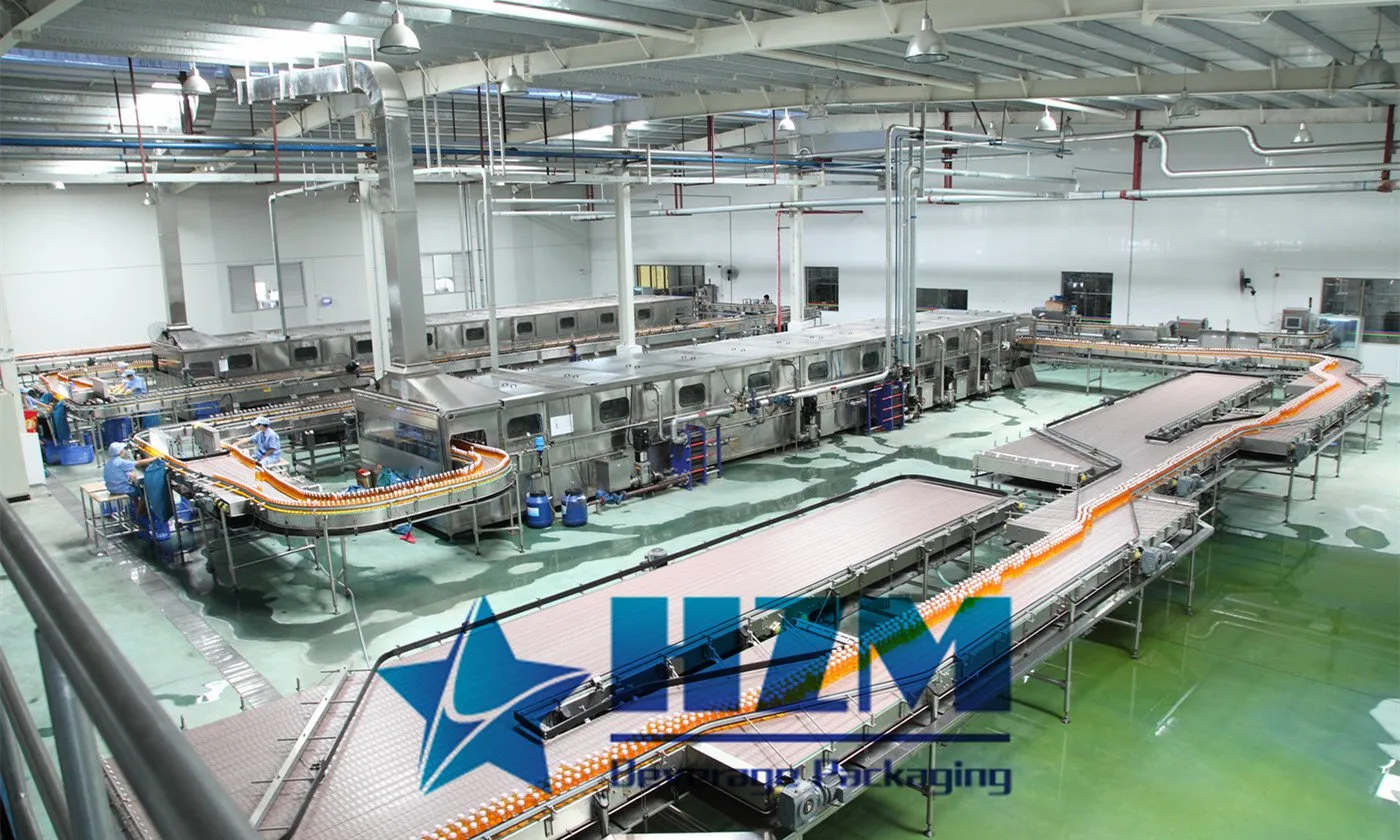
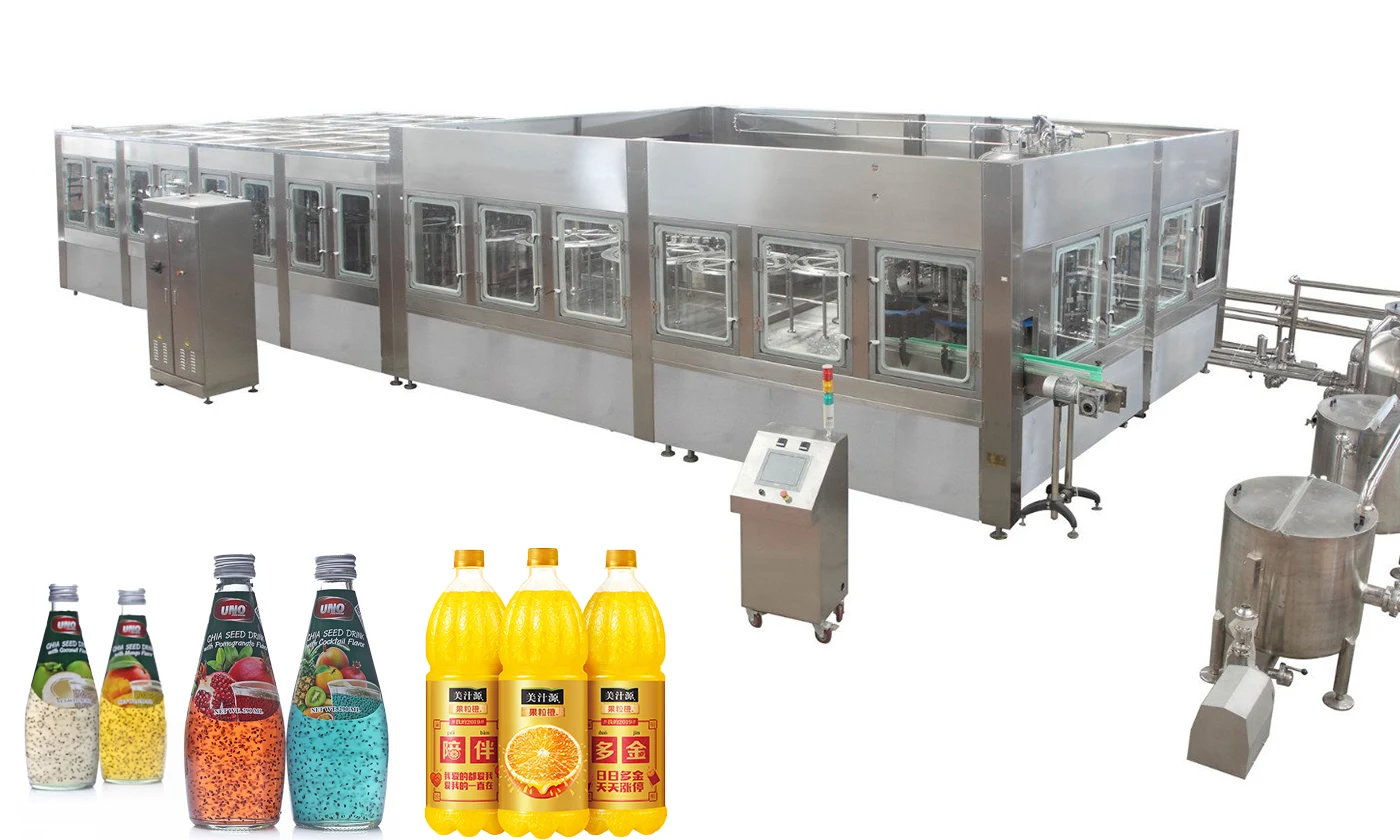
A detailed introduction of the production line process for juice beverages
- Raw material selection
- Fruit cleaning
- Crushing and pre-processing
- Juice extraction
- Coarse filtration
- Clarification and fine filtration
- Homogenization and deaeration
- Concentration
- Sterilization
- Packaging
- Second sterilization
Ⅰ.Selection of Fruit Raw Materials

arrangement of fresh fruits from market over wooden planks
1.Ripeness of Fruit and Vegetable Raw Materials:
Fruit juices made from unripe or poorly developed fruit and vegetable raw materials have much lower levels and poorer quality of aromatic components compared to those made from well-grown ripe fruit as raw materials. Similarly, fruit and vegetable juice drinks made from such raw materials often have poor flavor due to low sugar content and soluble solid content, and may even lack the normal flavor that a beverage should have. If fruit raw materials are too ripe, the flesh will be too soft or completely overripe (lacking juice), and the original pectin in the raw materials will transform into water-soluble pectin, making juice extraction and clarification difficult, resulting in a decrease in juice yield and even raw material spoilage. Fruit raw materials that have reached the optimal processing ripeness have external characteristics that are between the harvest ripeness and quality ripeness.
2.Freshness of Fruit and Vegetable Raw Materials:
For pit fruit raw materials harvested when fully mature on the tree, they are generally stored for about 2 weeks to improve their quality, while fresh fruits and vegetables are best juiced immediately, and if not used immediately, they must be stored in deep freeze (-18℃ or below).
3.Integrity and Undamagedness of Fruit and Vegetable Raw Materials
To ensure the quality of the original fruit and vegetable juice, the raw materials used should be undamaged, not spoiled, and free of pests.
II. Cleaning of Fruits
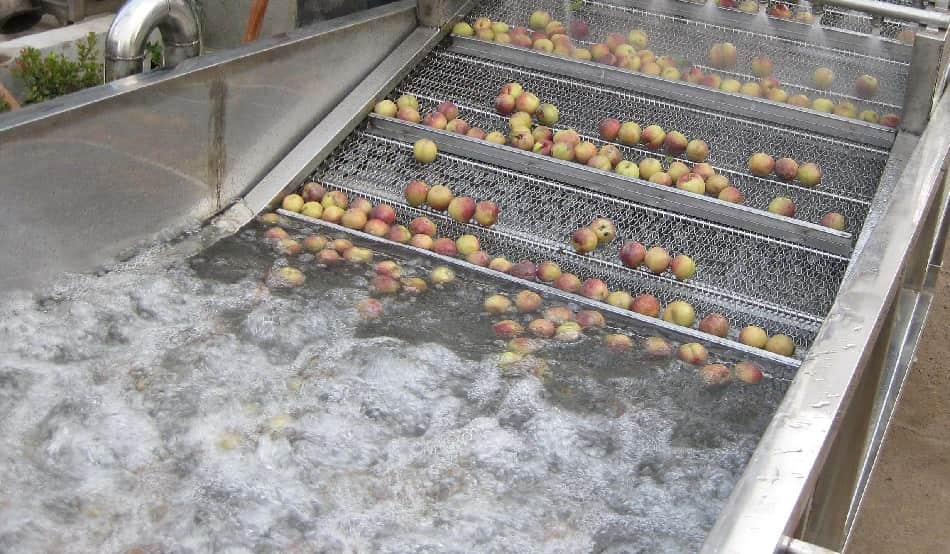

General procedures for cleaning: water conveyor → soaking → brushing → high-pressure spraying
Purpose: To remove dirt, sand, microorganisms, pesticide residues, and any leaves and branches carried on the surface of fruits and vegetables.
Note: The cleaning process is not necessary for processing berries and other small fruits.
Cleaning methods: soaking, bubble cleaning, water spraying, and chemical solution cleaning.
III. Crushing and Pretreatment
Purpose: The juice of fruits and vegetables is contained within the cells of their tissues. Only by breaking the cell walls can the juice and soluble solids inside the cells be extracted. Especially for fruits and vegetables with thick skin and dense flesh, crushing treatment is necessary to increase the juice yield.
Types of crushers: roller crushers (extrusion crushers) and hammer crushers (serrated crushers).
IV. Juice Extraction

Juice extraction is a crucial step in the processing of fruit and vegetable juices. Depending on the type of raw materials and the desired product form, there are different methods of juice extraction, including pressing, centrifugation, and extraction.
- Pressing: A widely used method of juice extraction that involves applying pressure to fruits and vegetables to extract their juice. Cold pressing, hot pressing, and even frozen pressing can be used. The process of extracting juice from fruits and vegetables or fruit pulp using external mechanical pressure is called pressing.
Suitable for: Apples, cherries, grapes, etc.
- Centrifugation: The juice is separated from the pulp using a horizontal spiral centrifuge.
- Extraction: Suitable for dried fruits such as sour dates, umeboshi, red dates, and fruits with a high pectin content, such as hawthorn. There are two types of extraction methods: batch and continuous.
Suitable for: Dried fruits such as sour dates, umeboshi, red dates, etc.
- Pulping: Suitable for the production of fruit and vegetable pulps and purees.
V. Coarse Filtration
Except for the pulping method, other methods of juice extraction produce a large amount of suspended particles, such as meat fibers, fruit skin, and fruit pits. Their presence affects the appearance and flavor of the final product and needs to be removed promptly. Coarse filtration can be carried out during juice extraction or as a separate operation. In production, a vibrating screen is usually used for coarse filtration.
VI. Clarification and Fine Filtration
Removes all suspended particles and gel particles that can easily form sediment.
VII. Homogenization and Deaeration of Fruit and Vegetable Juice
Homogenization: further breaks down and refines the suspended fruit pulp particles in the fruit and vegetable juice, making them more uniform in size, while promoting the dissolution of pectin on the fruit pulp cell walls, and distributing the pectin uniformly in the fruit and vegetable juice, forming a homogeneous and stable dispersion system.
If not homogenized, the suspended fruit pulp particles in the fruit and vegetable juice will be relatively large and the product will be unstable. The fruit pulp will gradually sink to the bottom of the container under the effect of gravity. After being left for a period of time, layering will occur with distinct boundaries. The upper part of the container will be relatively clear, while the lower part will be turbid, affecting the appearance and quality of the product.
Applicable to: turbid juice and meat-containing beverages.
Equipment used: high-pressure homogenizer, ultrasonic homogenizer, colloidal mill, etc.
Deaeration: A certain amount of air is dissolved in the fruit and vegetable tissue. During processing, a large amount of air is introduced into the fruit and vegetable juice through crushing, juicing, homogenization, pumping, and pipeline transportation. In the production process, it is necessary to remove these dissolved air, which is called deaeration or oxygen removal. Deaeration can reduce or avoid the oxidation of fruit and vegetable juice, reduce the destruction of color, flavor, and nutrients, such as the oxidation of vitamin C, prevent the oxidation and corrosion of tinplate cans, prevent suspended particles from adsorbing gas and floating up, and prevent foam during filling and sterilization.
VIII. Concentration of Fruit and Vegetable Juice
Concentration: removing some water, increasing stability, reducing volume, and meeting the needs of other beverage production.
The main methods of fruit and vegetable juice concentration are:
- Vacuum concentration method
- Reverse osmosis concentration method
- Freeze concentration method
Ⅸ.Sterilization of Fruit and Vegetable Juice
Sterilization: mainly refers to killing pathogenic bacteria in fruit and vegetable juice and inactivating enzymes in the juice.
The correct sterilization process of fruit and vegetable juice and its beverages not only affects the preservation of the products but also the quality of the products, which is a very important issue. Heating can kill bacteria, molds, and yeasts that cause spoilage in fruits and vegetables, and at the same time, inactivate the activity of enzymes. By using appropriate heating temperature and time, the purpose of killing microorganisms can be achieved. However, to minimize the impact on the quality of fruit and vegetable juice, it is necessary to choose reasonable heating temperature and time.
Sterilization methods:
- Heat sterilization
- Pasteurization (LTS)
- High-temperature short-time sterilization (HTST)
- Ultra-high temperature instantaneous sterilization (UHTS)
Non-heat sterilization:
High pressure, pulse, ultraviolet, oscillating magnetic field
In production, general sterilization method can be used, which is to sterilize at 80-85 ℃ for about 30 minutes, and then cool it in cold water to achieve sterilization. However, due to the long heating time, the color and flavor of fruit and vegetable juice are lost, especially for cloudy juice, which is easy to produce a cooked flavor. Therefore, the high-temperature instantaneous sterilization method is often used, which is to sterilize at 93 ℃ ± 2 ℃ for 15-30 seconds. In special cases, a temperature of above 120 ℃ can be used to hold for 3-10 seconds for sterilization.
Experimental results have shown that high-temperature instantaneous sterilization method is widely used for the same sterilization effect.
Ⅹ.juice Canning
Canning methods: hot filling, cold filling, aseptic filling.
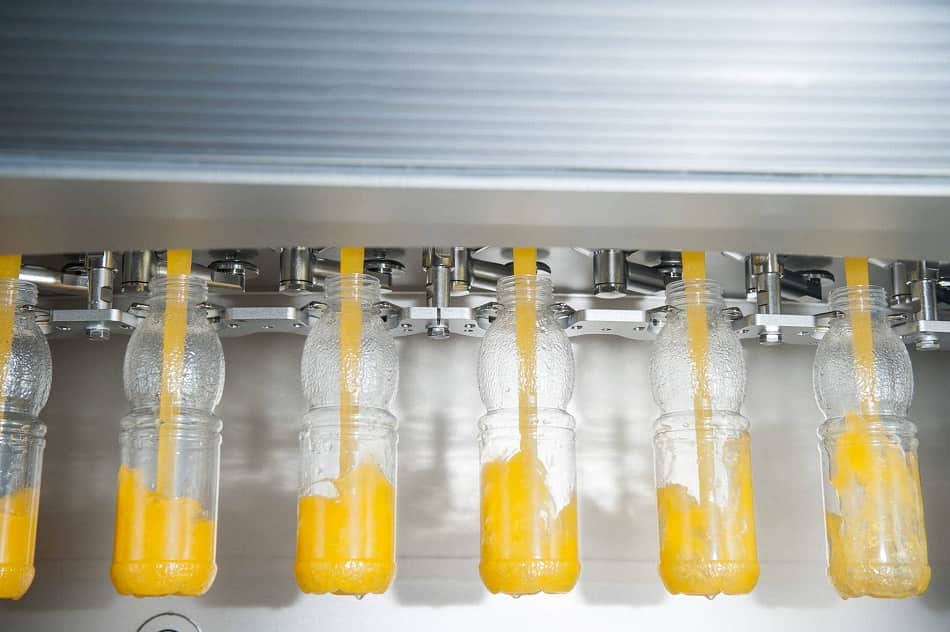

- Hot filling: After the fruit and vegetable juice is heat-sterilized, it is not cooled but is filled while hot, using the heat of the juice to sterilize the inner surface of the container. If the seal is intact, it can continue to maintain a sterile state. However, the time required between sterilization and filling is usually more than 3 minutes. Therefore, it is difficult to avoid quality deterioration caused by heat.
- Cold filling: After the fruit and vegetable juice is heat-sterilized, it is immediately cooled to 5°C and filled and sealed. After heating the juice to the sterilization temperature, it is kept for a certain time, then immediately cooled to room temperature or below using a heat exchanger. The cooled fruit and vegetable juice is then filled. The heat has a minimal effect on the quality of the juice, and high-quality products can be obtained. However, all operations after sterilization and cooling should be carried out under aseptic conditions.
- Aseptic filling: After the fruit and vegetable juice is heat-sterilized, it is filled in aseptic conditions, and the product is sold at room temperature, which can be stored for more than 6 months.
- Use of equipment: Hot Filling Machine
- Canning and sterilization precautions: sterilization temperature, filling temperature, packaging container, circulation temperature, and shelf life.
Ⅺ.Secondary sterilization
In actual factory production, the process conditions including temperature and time management are often not strict enough, and the filling temperature before and after batch ingredients are not consistent, and the container cover is not thoroughly disinfected. After the beverage is canned, the packaging cannot achieve a commercial sterile state, which often leads to microbial spoilage of fruit and vegetable juices and beverages, causing significant losses. Therefore, sterilization is still required after canning and sealing.
Canned fruit and vegetable juices can also be subjected to a 20-30 minute Pasteurization at 80-85°C after heating, canning, and sealing. The sterilization time depends on the size of the can, and the product should be cooled promptly after sterilization. The conditions for secondary sterilization after canning should be appropriately reduced.
TAG: Filling Machine Hot Filling Machine Juice Filling Machine
Core Selling Points of Glass Bottle CSD Filling & Capping Line
Differences Between Hot Filling and Cold Filling in Beverage Filling Machines
juice box making machine : Factory direct selling price
Optimization of Juice Beverage Production Line Process and Discussion on Cold vs. Hot Filling
What are the safety risks of liquid filling machines? How to avoid them?
How to Choose a Fruit Juice Beverage Production Line
-
![Beverage Packaging Machine for Juice, Soft Drinks, Carbonated Drinks, and Energy Drink]()
Beverage Packaging Machine for Juice, Soft Drinks, Carbonated Drinks, and Energy Drink
-
![Glass Bottle CSD & Water Drinks Filling Machine]()
Glass Bottle CSD & Water Drinks Filling Machine
-
![Automatic 5 Gallon Water Filling Line | 3-5 Gallon Bottled Water Production Line Manufacturer]()
Automatic 5 Gallon Water Filling Line | 3-5 Gallon Bottled Water Production Line Manufacturer
-
![Automatic PET Bottle Blowing Filling Capping Machine – Best price beverage machinery]()
Automatic PET Bottle Blowing Filling Capping Machine – Best price beverage machinery
-
![PET Bottle Edible Oil Bottling Line | Automatic Rotary Type Edible Oil Filling Machine]()
PET Bottle Edible Oil Bottling Line | Automatic Rotary Type Edible Oil Filling Machine